Veganism is growing in popularity, and you might be curious about why. It’s not just about healthier eating—it’s also about improving your overall well-being and making ethical choices. Vegan food, also known as plant-based food, includes vegetables, fruits, and dairy alternatives instead of meat. Research shows that following a vegan diet can lower the risk of heart disease, prevent type 2 diabetes, and avoid animal cruelty. In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know before starting your vegan journey.
What is Vegan?
Simply put, being vegan means avoiding all animal products in your diet. Some people take it further by not buying or using anything made from animals, like clothes, leather, or makeup, as they see it as a form of animal cruelty. While similar to vegetarians, vegans are different because vegetarians still consume products like milk, eggs, and honey that don’t require animal slaughter. If you’re thinking about becoming vegan for your health or other reasons, don’t worry—there are many supportive vegan communities to help you along the way.
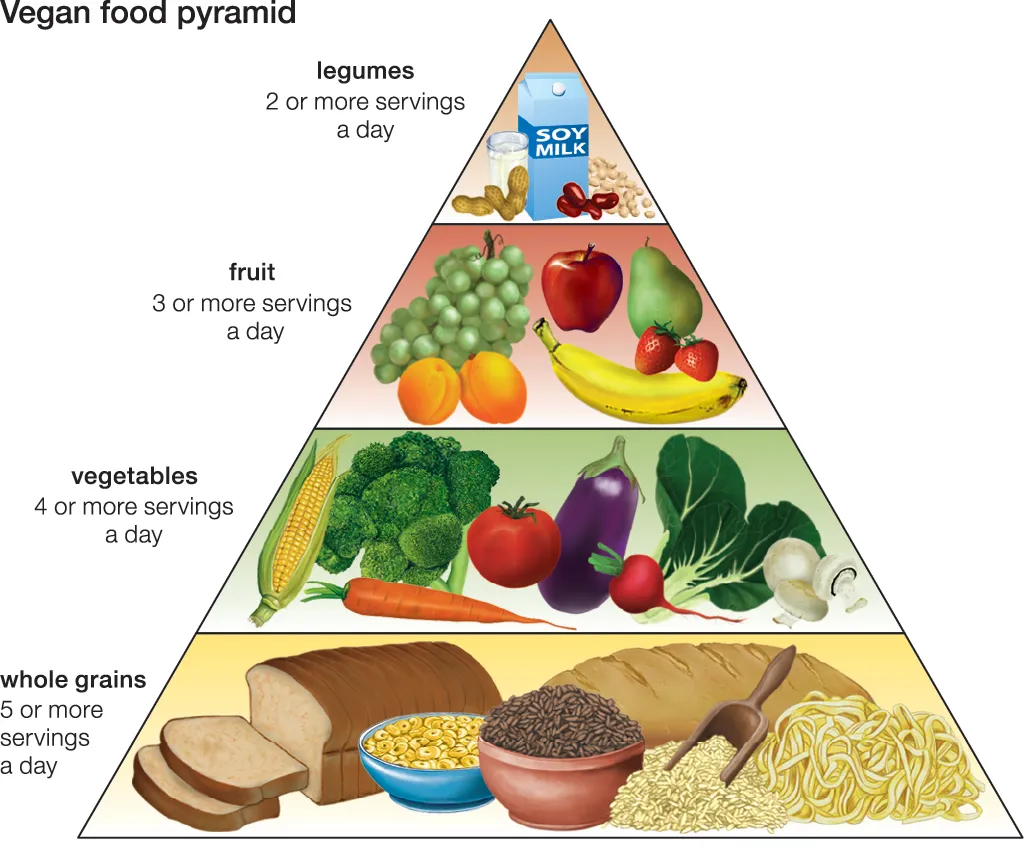
The Vegan Food Pyramid
If you’re curious about what vegans eat, the Vegan Food Pyramid is a simple guide. It helps you understand the key food groups for a balanced vegan diet.
At the bottom of the pyramid are whole grains like rice, oats, and bread. These provide energy and fiber. Above that are vegetables and fruits, which are packed with vitamins and should make up a large part of your meals. The next level includes legumes like beans and lentils, which are great for protein. You’ll also find nuts and seeds here, providing healthy fats.
At the top are plant-based fats, like olive oil and avocado, and fortified foods like plant milk, which give you nutrients like vitamin B12 and calcium. Following this pyramid helps vegans maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
 Why Go Vegan?
Why Go Vegan?
People choose to go vegan for health, ethical, and environmental reasons. A plant-based diet can improve overall health by lowering cholesterol, boosting heart health, and helping with weight management. Vegan diets are also rich in fiber and antioxidants, which can improve digestion compared to diets that include meat and dairy. These benefits make veganism an attractive option for those seeking a healthier lifestyle.
Transitioning from a non-vegan to a vegan diet can feel like a big change, but it doesn’t have to be difficult. Starting with small steps, such as replacing meat with plant-based proteins like tofu or beans, can make the process smoother. Many people find that gradually cutting out animal products while exploring new plant-based meals helps them adjust. Over time, this transition not only benefits personal health but also supports animal welfare and reduces the environmental impact of food production.
Can Vegan Food give us the Nurtritients that we need?
Yes, a well-planned vegan diet can provide all the essential nutrients your body needs. Plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Protein, which many people associate with animal products, can easily be found in vegan sources like beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh.
While most nutrients can be obtained from plant-based foods, there are a few nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids that vegans should pay attention to. Vitamin B12, for example, is found mainly in animal products, so vegans often rely on fortified foods or supplements to ensure they meet their needs. With proper planning and awareness, vegan diets can offer balanced nutrition that supports overall health and well-being.
Can Vegan Food Provide Enough Protein?
While meat is often seen as the top source of protein, there are plenty of plant-based options that provide enough protein for a healthy diet. Foods like beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa are excellent vegan protein sources. These foods are not only rich in protein but also come with added benefits like fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which meat lacks.
For example, a cup of cooked lentils provides about 18 grams of protein, and tofu offers around 10 grams per serving. By including a variety of these foods in your meals, you can easily meet your daily protein needs without relying on meat. Many athletes and bodybuilders even follow vegan diets and achieve their protein goals through careful meal planning.
Here’s a list of vegan foods that are rich in protein:
- Lentils (18g per cup, cooked)
- Tofu (10g per 1/2 cup)
- Chickpeas (15g per cup, cooked)
- Black beans (15g per cup, cooked)
- Quinoa (8g per cup, cooked)
- Tempeh (15g per 1/2 cup)
- Edamame (17g per cup, cooked)
- Seitan (21g per 3 oz)
- Hemp seeds (10g per 3 tablespoons)
- Almonds (6g per ounce)
Can Vegan Take Food Supplements?
Yes, vegans can take food supplements, and in some cases, it’s beneficial to ensure they’re getting all essential nutrients. While a well-balanced vegan diet covers most needs, some vitamins and minerals, like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, may require supplements.
Here are some examples of supplements suitable for vegans:
- NOW Vitamin B-50 mg, 250 Veg Capsules:
Provides essential B vitamins, including B12, which is important for energy and metabolism. Buy here - Secret Element Citrus Bergamot Extract 1000mg:
A natural supplement that supports healthy cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health. Buy here - Enzymedica Digest Basic, 90 Caps:
A digestive enzyme supplement to support better digestion, especially for those transitioning to a plant-based diet. Buy here - Nature’s Way Premium Herbal Siberian Eleuthero:
A herbal supplement that helps boost energy and improve overall vitality. Buy here
Incorporating supplements into a vegan diet can be a great way to ensure you’re meeting all your nutritional needs. With options like NOW Vitamin B-50, Secret Element Citrus Bergamot Extract, Enzymedica Digest Basic, and Nature’s Way Premium Herbal Siberian Eleuthero, vegans can easily maintain optimal health and energy levels. Just remember, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before adding new supplements to your routine.
Can Vegan Take Whey Protein?
No, vegans cannot take whey protein because it is derived from dairy, specifically the liquid byproduct of cheese production. Since whey is an animal product, it doesn’t align with a vegan diet. However, there are plenty of plant-based protein alternatives, such as pea protein, soy protein, and rice protein, which provide similar benefits without using animal-derived ingredients. These options are just as effective in meeting your protein needs while staying true to a vegan lifestyle.












Comments are closed.